What is Impermanent Loss

Simplifying Impermanent Loss
Decentralized Finance is one of the most exciting and revolutionary use cases of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency in the modern world. Financial tools and income generation strategies have become more accessible than ever before, with users enjoying greater control over their personal finances.
Despite this, the world of DeFi can be a dangerous minefield for those who don’t understand the basics. It’s crucially important to have a solid grasp of DeFi fundamentals, like liquidity pools, before diving too deep into the rabbit hole.
For most new users, one of the most commonly overlooked and misunderstood risks in decentralized finance is Impermanent Loss. In this brief article, we’ll break down and simplify the most common questions like ‘What is Impermanent Loss?’ and show you how to avoid it.
What is Impermanent Loss?
If you create a liquidity pair worth $100 and deposit it into a decentralized exchange or AMM, only to withdraw less than $100 after a month of collecting trading fees, chances are Impermanent Loss is to blame.
Impermanent Loss occurs when the ratio of two or more cryptos in a liquidity pool changes based on the price change of the individual asset. Because being a liquidity provider means you’re holding a percentage of the pool’s total assets, the ratio of tokens in your deposited pair will also change. As a rule of thumb, the greater the change in price of individual assets, the greater the impermanent loss.
How does Impermanent Loss Work?
To get a better understanding of how Impermanent Loss works, let’s go through a quick example.
Ben wants to create a liquidity pair using ETH and BUSD to earn passive income from trading fees. For the sake of simplicity, let’s imagine that 1 ETH=$1000.
Ben deposits 1 ETH and 1000 BUSD into the liquidity pool on PancakeSwap, which is also funded by other users. Ben’s deposit has a USD value of $2000. The total liquidity in the pool is 10 ETH and 10,000 BUSD and has a total liquidity of 10,000. Ben owns a 10% share of the pool.
While Ben’s assets are deposited in the pool, the price of ETH explodes to 4000 BUSD. Because BUSD is a stablecoin pegged to the United States Dollar, its price hasn’t changed. During this time, arbitrage traders and other DeFi users add BUSD and remove ETH from the pool so that the pool’s ratio of ETH/BUSD reflects the current market price of ETH.
What’s important to remember is that the total liquidity hasn’t changed. However, the ratio of pooled tokens has changed. We now have less ETH in the pool, but more BUSD.
As a result, Ben’s 10% share of the pool will be different to what he’d initially deposited. After depositing 1 ETH and 1000 BUSD, Ben can now withdraw his 10% share, which includes 0.25 ETH and 2000 BUSD.
At the new market prices, 0.25 ETH and 2000 BUSD is valued at $3,000 USD. Ben’s happy with his $1,000 dollar gain. However, Ben’s original holdings were 1 ETH and 1000 BUSD, meaning that if he had simply held these assets in his own crypto wallet, they would be worth $5,000 USD.
How Much Can I Lose to Impermanent Loss?
Impermanent Loss occurs whether price change is positive or negative. The key factor that dictates the magnitude of Impermanent Loss is the ratio of tokens in the pool. A larger change results in a larger Impermanent Loss, compared to if you’d simply held your assets.
The rate of impermanent loss can be estimated using the graph below:
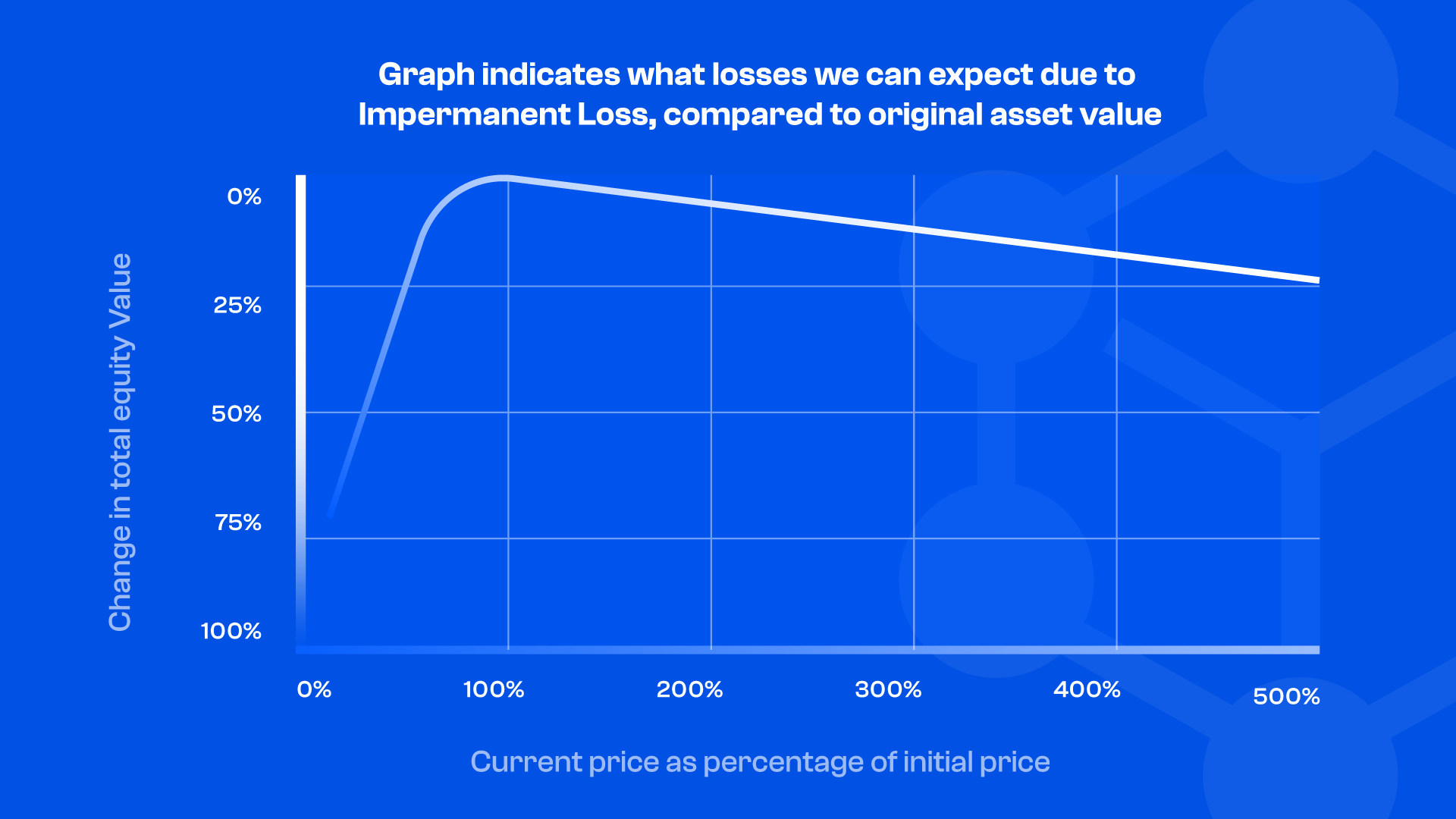
The graph indicates what losses we can expect due to Impermanent Loss, compared to original asset value:
- Asset price change of 1.25x = 0.6% loss
- Asset price change of 1.50x = 2.0% loss
- Asset price change of 1.75x = 3.8% loss
- Asset price change of 2x = 5.7% loss
- Asset price change of 3x = 13.4% loss
- Asset price change of 4x = 20.0% loss
- Asset price change of 5x = 25.5% loss
How to Avoid Impermanent Loss?
Fortunately, the benefits and incentives of providing liquidity counteract the risks of Impermanent Loss. In many cases, the rewards earned from trading fees outweigh the losses, resulting in a net positive for the provider.
Decentralized exchanges and other crypto projects also offer extra rewards in the form of token emissions to provide additional incentives for liquidity providers. This is called yield farming, and is an excellent strategy to earn free crypto tokens on top of the rewards collected from trading fees.
Another way to avoid impermanent loss and reduce your risk, while still reaping the benefits is to create liquidity pairs for assets with similar price movements. For example, Bitcoin (BTC) is often considered as a price magnet for the entire cryptocurrency market. Most coins follow BTC’s price movement, meaning that the ratio of assets in a pool with BTC often change less than if they were paired to stablecoins like BUSD or USDT.
Another strategy to avoid Impermanent Loss is to create liquidity pairs using stablecoins. Because stablecoins are pegged to the United States Dollar, their price rarely deviates far from each other, allowing you to collect trading fees with drastically reduced risk of Impermanent Loss.
Summary
While liquidity provision and yield farming is a great method to passively grow your portfolio, Impermanent Loss is a constant risk that must be considered and planned for. Making strategic decisions around when and where you deposit liquidity can help you protect your assets, while still earning crypto rewards.
Decentralized Finance is truly the land of opportunity for users who are able to manage their risk effectively. By educating yourself on the most effective yield generation strategies, you can find profitable and low-risk opportunities and enjoy greater convenience and control of your assets.




